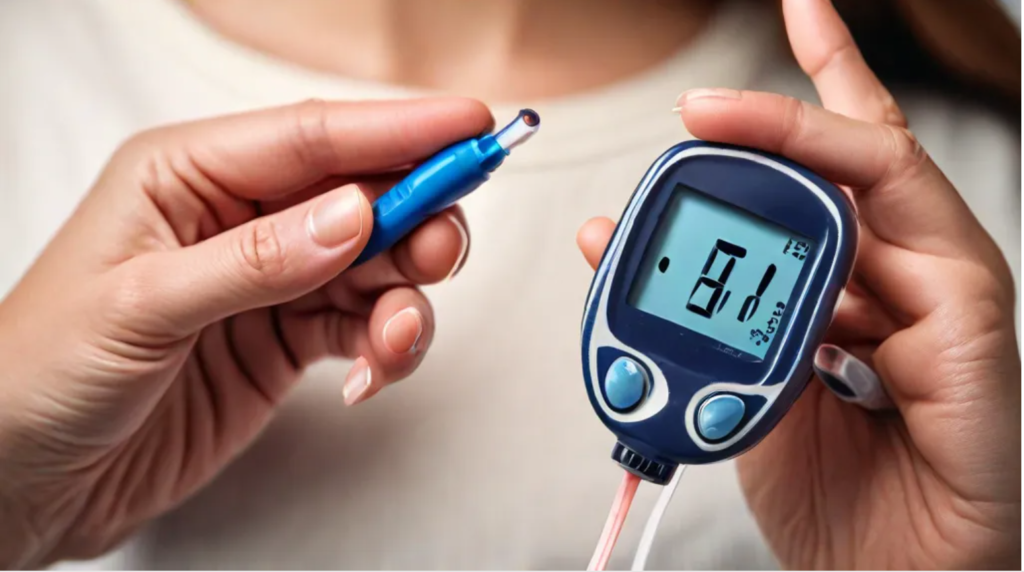
Diabetes is a serious condition that affects many people worldwide. It is important to understand what causes diabetes. This helps us stay fit and healthy.
Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease. This means the body attacks its own insulin-producing cells. Insulin helps move sugar from the blood into cells for energy. Without it, sugar builds up in the blood. This can cause many health problems. Type 1 diabetes often starts in childhood. No one knows exactly why the body attacks its own cells, but genetics and environment play a role.
Symptoms of Type 1 diabetes include extreme thirst, frequent urination, sudden weight loss, and fatigue. These symptoms can appear suddenly. If not treated, Type 1 diabetes can lead to serious complications like diabetic ketoacidosis, which is life-threatening. People with Type 1 diabetes need to monitor their blood sugar levels closely and take insulin injections daily.
Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is the most common type of diabetes. It usually starts in adults, but kids can get it too. In Type 2 diabetes, the body does not use insulin well. This is called insulin resistance. Over time, the body may not make enough insulin. Type 2 diabetes is linked to lifestyle choices and genetics. Poor diet, lack of exercise, and being overweight increase the risk.
Type 2 diabetes develops gradually. Symptoms may be mild and go unnoticed for a long time. They include increased thirst, frequent urination, and fatigue. High blood sugar levels can cause serious health problems over time. These include heart disease, nerve damage, kidney issues, and vision problems. Managing Type 2 diabetes involves healthy eating, regular exercise, and sometimes medication.
Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes happens during pregnancy. The body cannot make enough insulin for both the mother and baby. This type usually goes away after the baby is born. But, it increases the risk of Type 2 diabetes later in life. Pregnant women should have regular check-ups to monitor their blood sugar levels.
Gestational diabetes can affect the baby’s health too. Babies may grow larger than normal, leading to complications during birth. There’s also a higher risk of developing obesity and Type 2 diabetes later in life. Managing gestational diabetes involves diet, exercise, and sometimes insulin. Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels is essential during pregnancy to ensure the health of both mother and baby.
Prediabetes
Prediabetes means blood sugar levels are higher than normal but not high enough to be diabetes. It is a warning sign. Without lifestyle changes, it can lead to Type 2 diabetes. Healthy eating and regular exercise can help prevent it.
Prediabetes often shows no symptoms. It’s usually discovered through routine blood tests. If you have prediabetes, you are at a higher risk for heart disease and stroke. Making lifestyle changes now can prevent more serious health problems later. Eating a balanced diet, maintaining a healthy weight, and staying active are key to reversing prediabetes.
Other Causes of Diabetes
Several other factors can contribute to the development of diabetes:
- Genetics: A family history of diabetes increases the risk.
- Age: The risk of Type 2 diabetes increases with age.
- Ethnicity: Certain ethnic groups, such as African Americans, Hispanics, and Asians, are at a higher risk.
- Medical Conditions: Conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and high blood pressure are linked to a higher risk of diabetes.
- Medications: Certain medications, like steroids, can increase blood sugar levels and lead to diabetes.
The Role of Fitness
Fitness plays a crucial role in managing diabetes. Here are some ways it helps:
- Weight Control: Maintaining a healthy weight helps manage blood sugar levels.
- Improved Insulin Sensitivity: Exercise helps your body use insulin better.
- Increased Energy: Regular activity keeps you energetic and improves your mood.
Exercise has numerous benefits for people with diabetes. Aerobic exercises, like walking or swimming, improve heart health. Strength training, like lifting weights, builds muscle and boosts metabolism. Flexibility exercises, like yoga, enhance balance and reduce stress.
Regular physical activity can also prevent or delay the onset of Type 2 diabetes. It helps control blood sugar levels and reduces the risk of complications. Incorporate both aerobic and strength training exercises into your routine for maximum benefits.
Conclusion
Understanding the causes of diabetes helps in managing it better. Knowledge, healthy habits, and fitness are essential. With the right approach, you can lead a healthy and active life. Knowing the different causes of diabetes helps tailor your lifestyle and treatment plan. Education and support from healthcare professionals are crucial. By staying informed and proactive, you can take control of your health and reduce the risk of complications.
FAQ
Q: Can Type 1 diabetes be prevented?
A: Type 1 diabetes cannot be prevented, but it can be managed with proper treatment and care.
Q: Is gestational diabetes permanent?
A: Gestational diabetes usually goes away after childbirth, but it increases the risk of Type 2 diabetes later.
Q: Can lifestyle changes reverse prediabetes?
A: Yes, with healthy lifestyle changes, prediabetes can be reversed or delayed.
Q: What types of exercise are good for diabetes?
A: Aerobic exercises like walking and cycling, and strength training exercises are beneficial.
Q: How often should I check my blood sugar levels?
A: It depends on your treatment plan. Your doctor will guide you on how often to check.
Q: What are the complications of unmanaged diabetes?
A: Unmanaged diabetes can lead to serious complications, such as heart disease, kidney damage, nerve damage, and eye problems. It’s important to manage your condition to prevent these complications.
Q: Can children get Type 2 diabetes?
A: Yes, children can get Type 2 diabetes, especially if they are overweight and inactive. Healthy eating and regular physical activity are important for prevention.
Q: Are there other types of diabetes?
A: Yes, there are other less common types, such as monogenic diabetes and cystic fibrosis-related diabetes. These types have different causes and require specific treatment.
Staying informed and active is key to managing diabetes. Keep learning and stay fit for a healthier future! 😊
I hope this longer version meets your needs. Let me know if there’s anything else you’d like to add!