Type 1 diabetes is a tough condition many people face. It happens when the body can’t make insulin. Insulin helps control blood sugar levels. Without it, blood sugar gets too high. Understanding this condition is important for everyone, not just diabetics.
The Basics of Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes is often diagnosed in children and young adults. It’s an autoimmune disease. This means the body’s own immune system attacks the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. This makes it different from type 2 diabetes, which usually happens due to lifestyle factors and genetics.
Warning Signs
Knowing the warning signs is key. Here are some to watch for:
- Frequent Urination: Diabetics might go to the bathroom a lot. When there’s too much glucose in the blood, kidneys go into overdrive to filter and absorb the excess. This process requires fluids, hence the frequent trips to the bathroom.
- Extreme Thirst: Feeling very thirsty all the time. This could be because your body is losing a lot of water through frequent urination. Dehydration becomes a problem, causing you to drink more. If you find yourself drinking unusually large amounts of water, it might be time to check your blood sugar levels.
- Increased Hunger: Always feeling hungry, even after eating. High blood sugar levels can make you feel like you need to eat more, even if you just ate. This is because your body isn’t using the insulin it produces efficiently, leading to fluctuating energy levels and an increased appetite.
- Weight Loss: Losing weight without trying. When your body can’t use sugar for energy, it starts to burn fat instead. This leads to unexplained weight loss, even when you maintain your usual diet. For diabetics, this is often a red flag that something is wrong with how the body is processing energy.
- Fatigue: Feeling very tired and weak. Your body might not be getting enough energy from sugar, making you feel weak and tired. Without efficient insulin use, your cells don’t get the glucose they need for energy, leading to chronic fatigue.
- Blurred Vision: Seeing things out of focus. High blood sugar levels can make your vision blurry. Excess glucose can cause the lenses of your eyes to swell, leading to temporary vision changes. If left unmanaged, it can also cause long-term damage to your eyesight.
- Slow-Healing Wounds: Cuts and bruises taking longer to heal. High blood sugar can slow down the healing process. Diabetics often experience delayed healing because high glucose levels affect circulation and the body’s ability to repair itself effectively.
- Frequent Infections: Getting sick more often. High blood sugar can make it harder for your body to fight infections. Diabetics are more susceptible to infections, particularly in the skin and urinary tract. The immune system is weakened, making it easier for infections to take hold.
- Tingling or Numbness: Feeling tingles or numbness in hands or feet. This can happen if diabetes affects your nerves. Known as nephropathy, this condition is caused by long-term high blood sugar levels damaging the nerves, particularly in the extremities.
- Dark Skin Patches: Noticing dark areas on the skin. This can be a sign of insulin resistance, which is linked to diabetes. These patches, often found in body folds like the neck or armpits, are known as acanthus nigricans and indicate that your body is struggling to regulate blood sugar effectively.
Managing Type 1 Diabetes
Managing type 1 diabetes is a daily task. It includes monitoring blood sugar levels and taking insulin. Eating a balanced diet and regular exercise also help keep blood sugar levels in check. For diabetics, it’s about balancing these elements to avoid high or low blood sugar.
Blood Sugar Monitoring
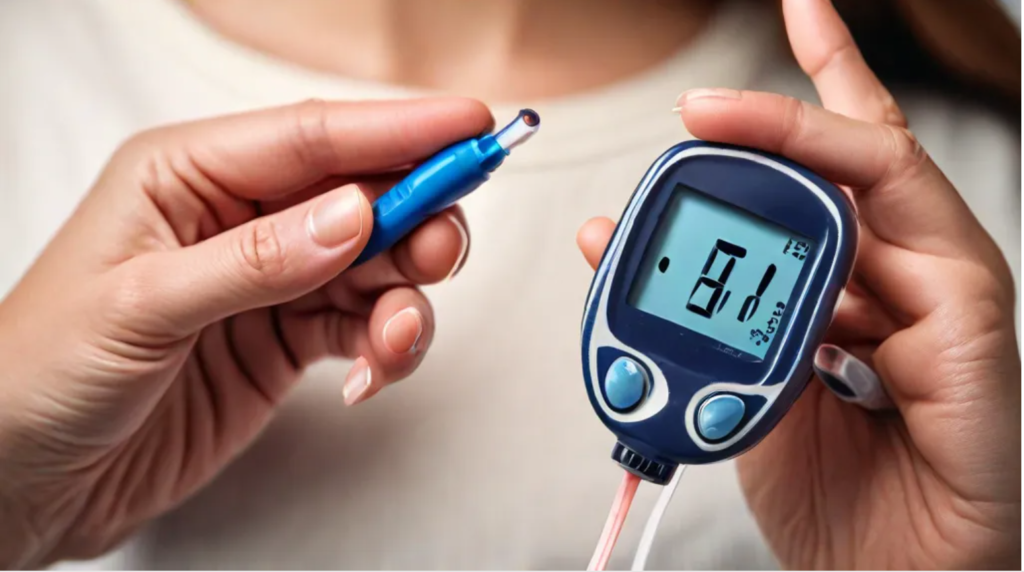
Checking blood sugar levels regularly is crucial. Diabetics need to know their blood sugar levels to manage their condition properly. This can be done with blood sugar meters or continuous glucose monitors (CGMs). CGMs provide real-time data and alerts, making it easier to track and manage blood sugar levels.
Insulin Therapy
Since their body can’t produce insulin, diabetics need insulin therapy. This can be through injections or an insulin pump. The goal is to mimic the natural insulin production as closely as possible. Insulin comes in different types, such as rapid-acting, short-acting, intermediate-acting, and long-acting, each serving a specific purpose in blood sugar management.
Diet and Exercise
A balanced diet helps manage blood sugar. Diabetics should eat a variety of foods, including fruits, vegetables, proteins, and whole grains. Counting carbohydrates is crucial because carbs directly impact blood sugar levels. Exercise is also important. It helps the body use insulin better and lowers blood sugar levels. Regular physical activity can also improve overall health and reduce the risk of complications associated with diabetes.
Complications of Type 1 Diabetes
Without proper management, type 1 diabetes can lead to serious complications. These include:
- Heart Disease: Increased risk of heart attacks and strokes.
- Kidney Damage: Diabetes can damage the kidneys’ filtering system, leading to kidney failure.
- Eye Damage: High blood sugar can damage blood vessels in the eyes, leading to vision problems or blindness.
- Nerve Damage: Neuropathy can cause pain, tingling, or numbness in the extremities.
- Foot Damage: Poor circulation and nerve damage increase the risk of foot infections and, in severe cases, amputation.
Living with Type 1 Diabetes
Living with type 1 diabetes requires planning and effort. But with the right tools and support, diabetics can lead healthy, full lives. It’s about staying informed, being proactive, and finding a routine that works. Building a support network of family, friends, and healthcare professionals is essential. Education about the condition and staying updated on new treatments can also make a big difference.
Conclusion
Type 1 diabetes is a complex challenge, but knowing the signs and how to manage it makes a big difference. Diabetics can live healthy lives with proper care. Awareness and education are key. If you notice any warning signs, see a doctor. Early detection and management are crucial.
FAQ’s
Q: Can anyone get type 1 diabetes?
A: Yes, anyone can get type 1 diabetes. It’s more common in children and young adults, but it can happen at any age.
Q: How is type 1 diabetes diagnosed?
A: Type 1 diabetes is diagnosed through blood tests that measure blood sugar levels. Tests like the fasting plasma glucose test, A1C test, and glucose tolerance test help in diagnosing the condition.
Q: Is there a cure for type 1 diabetes?
A: There’s no cure, but it can be managed with insulin therapy, diet, and exercise. Researchers are working on finding a cure, but for now, effective management is crucial.
Q: What should I do if I have symptoms?
A: See a doctor right away. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial. Managing blood sugar levels can prevent complications and improve quality of life.
Q: How can I support someone with type 1 diabetes?
A: Be understanding and supportive. Learn about the condition and help them manage their daily routine. Encourage healthy eating, exercise, and regular medical check-ups.
Understanding type 1 diabetes helps everyone. It’s important to recognize the signs and know how to manage this condition. Stay informed and support those who are living with it. By doing so, you can contribute to better health and wellbeing for yourself and others.