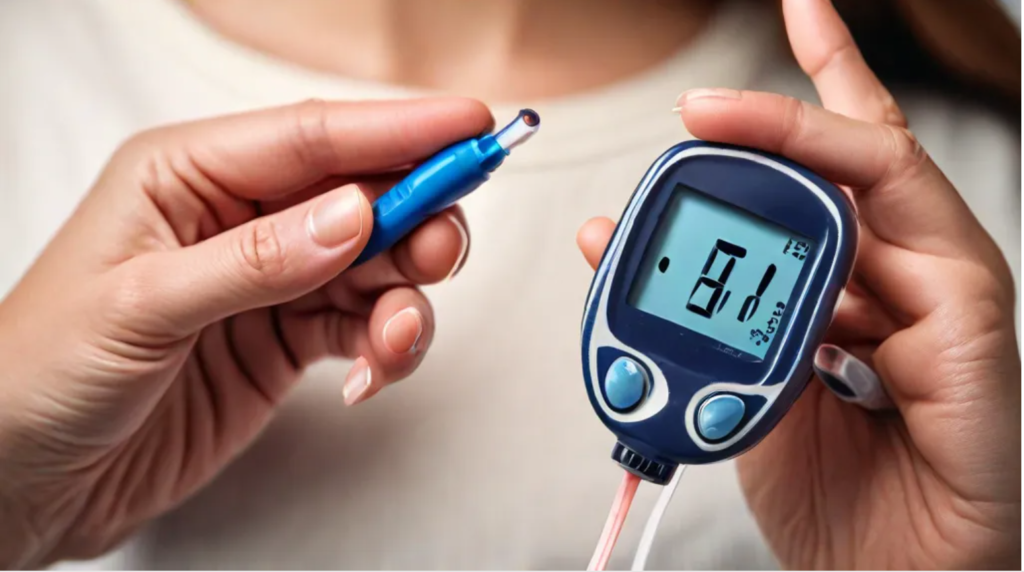
Diabetes, a chronic condition that disrupts the body’s ability to regulate blood sugar, casts a long shadow over millions of lives worldwide. This insidious disease, often hide silently, can lead to a host of serious complications if left unchecked. If you check it regularly lead a routine life diabetes does not harm you anything.
The Silent Saboteur
Diabetes, a stealthy intruder, often reveals its presence subtly. Symptoms can be mild and easily overlooked, leading to delayed diagnosis and potential health risks. Common signs include:
- Frequent Urination: A relentless urge to visit the bathroom, especially at night.
- Excessive Thirst: A persistent feeling of dryness, no matter how much water is consumed.
- Blurred Vision: A temporary impairment of eyesight, often fluctuating.
- Unexplained Weight Loss: A noticeable decrease in body weight without intentional dieting or increased physical activity.
- Slow-Healing Sores: Cuts, scrapes, or infections that take longer than usual to heal.
- Fatigue: A persistent feeling of tiredness and exhaustion.
- Increased Hunger: A constant craving for food, even after meals.
The Culprits Behind Diabetes
Several factors contribute to the development of diabetes:
- Genetics: A family history of diabetes can increase an individual’s susceptibility.
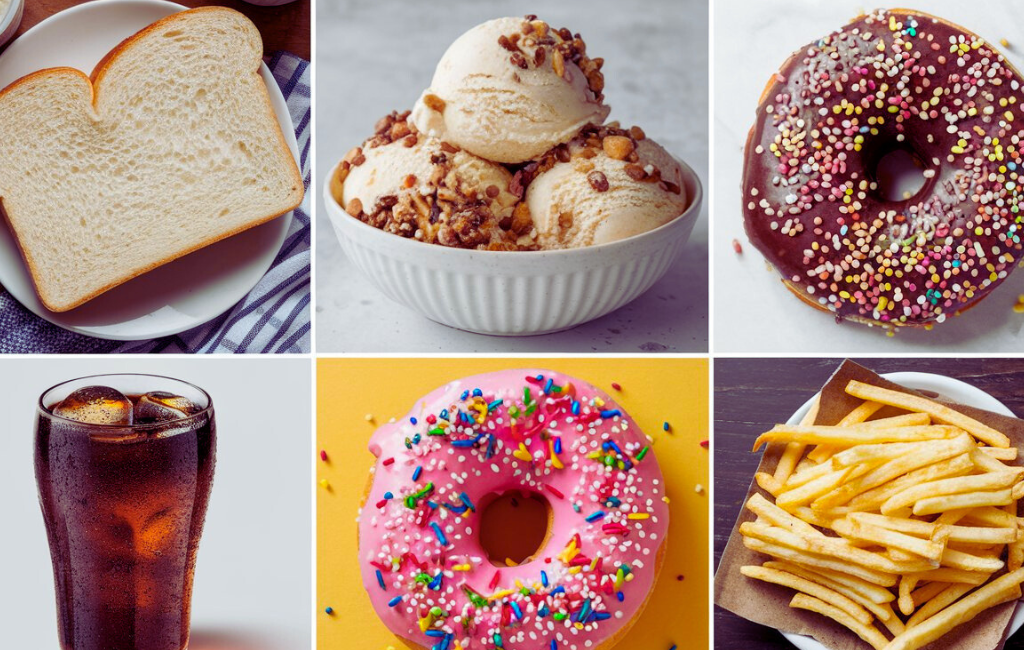
- Lifestyle: Unhealthy dietary habits, sedentary lifestyle, and obesity are significant risk factors.
- Insulin Resistance: The body’s cells become less responsive to insulin, impairing glucose uptake.
- Autoimmune Disorders: In type 1 diabetes, the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas.
Types of Diabetes: A Delicate Balance
Diabetes manifests in various forms:
- Type 1 Diabetes: An autoimmune condition where the body’s immune system destroys insulin-producing cells in the pancreas.
- Type 2 Diabetes:1 A more common type characterized by insulin resistance and insufficient insulin production.
- Gestational Diabetes: A temporary form of diabetes that develops during pregnancy.
Navigating the Path to Wellness
Managing diabetes requires a multifaceted approach, encompassing lifestyle modifications and medical interventions:
- Dietary Adjustments: A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help regulate blood sugar levels.
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity, such as brisk walking, swimming, or cycling, improves insulin sensitivity and aids in weight management.
- Medication: Oral medications or insulin therapy may be necessary to control blood sugar levels.
- Self-Monitoring: Regular blood sugar testing helps individuals track their glucose levels and make informed decisions about their treatment plan.
The Long-Term Impact
Uncontrolled diabetes can lead to a cascade of serious health complications:
- Heart Disease: Increased risk of heart attacks and strokes.
- Kidney Disease: Damage to the kidneys, potentially leading to kidney failure.
- Nerve Damage: Numbness, tingling, and pain in the extremities.
- Eye Damage: Vision impairment and potential blindness.
- Amputations: In severe cases, amputation of toes, feet, or legs may be necessary.
Conclusion of diabetes
Diabetes, a complex and multifaceted condition, demands vigilant management. By understanding the risk factors, symptoms, and treatment options, individuals can take proactive steps to prevent or control the disease. A healthy lifestyle, regular medical check-ups, and adherence to treatment plans are essential in mitigating the long-term consequences of diabetes.
FAQ’s
- Can diabetes be cured? While there’s currently no cure for diabetes, it can be effectively managed with proper treatment and lifestyle modifications.
- Is diabetes hereditary? Genetics play a role in the development of diabetes, but lifestyle factors also contribute significantly.
- What are the long-term complications of diabetes? Diabetes can lead to serious health problems, including heart disease, kidney disease, nerve damage, eye damage, and amputations.
- Can people with diabetes live a normal life? Absolutely! With diligent management, people with diabetes can live fulfilling and active lives.
- What is the best diet for people with diabetes? A balanced diet low in sugar and carbohydrates, rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins, is beneficial for managing diabetes.